Digital image processing using matlab: basic transformations, filters and operators
- 1. NATIONAL CHENG KUNG UNIVERSITY Inst. of Manufacturing Information & Systems DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING AND SOFTWARE IMPLEMENTATION HOMEWORK 1 Professor name: Chen, Shang-Liang Student name: Nguyen Van Thanh Student ID: P96007019 Class: P9-009 Image Processing and Software Implementation Time: [4] 2 4
- 2. 1 Table of Contents PROBLEM................................................................................................................................................................. 2 SOLUTION................................................................................................................................................................ 3 3.2.1 Negative transformation ............................................................................................................................ 3 3.2.2 Log transformation..................................................................................................................................... 3 3.2.3 Power-law transformation ......................................................................................................................... 4 3.2.4 Piecewise-linear transformation ................................................................................................................ 7 3.3.1 Histogram equalization.............................................................................................................................10 3.4.2 Subtraction ...............................................................................................................................................12 3.6.1 Smoothing Linear Filters...........................................................................................................................14 3.6.2 Order-Statistics Filters..............................................................................................................................16 3.7.2 The Laplacian............................................................................................................................................17 3.7.3 The Gradient.............................................................................................................................................19
- 3. 2 PROBLEM 影像處理與軟體實現[HW1] 課程碼:P953300 授課教授:陳響亮 教授 助教:陳怡瑄 日期:2011/03/10 題目:請以C# 撰寫一程式,可讀入一影像檔,並可執行以下之影像 空間強化功能。 a. 每一程式需設計一適當之人機操作介面。 b. 每一功能請以不同方法分開撰寫,各項參數需讓使用者自行輸入。 c. 以C# 撰寫時,可直接呼叫Matlab 現有函式,但呼叫多寡,將列為評分考量。 (呼叫越少,分數越高) 一、 基本灰階轉換 1. 影像負片轉換 2. Log轉換 3. 乘冪律轉換 4. 逐段線性函數轉換 二、 直方圖處理 1. 直方圖等化處理 2. 直方圖匹配處理 三、 使用算術/邏輯運算做增強 1. 影像相減增強 2. 影像平均增強 四、 平滑空間濾波器 1. 平滑線性濾波器 2. 排序統計濾波器 五、 銳化空間濾波器 1. 拉普拉斯銳化空間濾波器 2. 梯度銳化空間濾波器
- 4. 3 SOLUTION Using Matlab for solving the problem 3.2.1 Negative transformation Given an image (input image) with gray level in the interval [0, L-1], the negative of that image is obtained by using the expression: s = (L – 1) – r, Where r is the gray level of the input image, and s is the gray level of the output. In Matlab, we use the commands, >> f=imread('Fig3.04(a).jpg'); g = imcomplement(f); imshow(f), figure, imshow(g) In/output image Out/in image 3.2.2 Log transformation The Logarithm transformations are implemented using the expression: s = c*log (1+r). In this case, c = 1. The commands, >> f=imread('Fig3.05(a).jpg'); g=im2uint8 (mat2gray (log (1+double (f)))); imshow(f), figure, imshow(g)
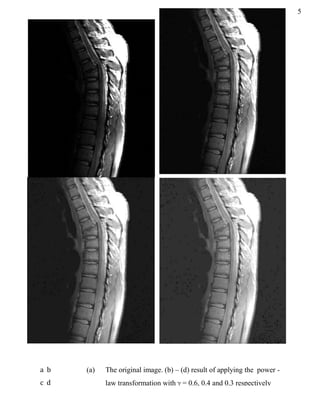
- 5. 4 In/output image Out/in image 3.2.3 Power-law transformation Power-law transformations have the basic form, s = c*r. ^, where c and are positive constants. The commands, >> f = imread ('Fig3.08(a).jpg'); f = im2double (f); [m n]=size (f); c = 1; gama = input('gama value = '); for i=1:m for j=1:n g(i,j)=c*(f(i,j)^gama); end end; imshow(f),figure, imshow(g); With = 0.6, 0.4 and 0.3 respectively, we can get three images respectively, as shown in the following figure,
- 6. 5 a b c d (a) The original image. (b) – (d) result of applying the power - law transformation with = 0.6, 0.4 and 0.3 respectively
- 7. 6 a b c d (a) The original image. (b) – (d) result of applying the power - law transformation with = 3, 4 and 5 respectively
- 8. 7 3.2.4 Piecewise-linear transformation Contrast stretching The commands, % function contrast stretching; >> r1 = 100; s1 = 40; r2 = 141; s2 = 216; a = (s1/r1); b = ((s2-s1)/ (r2-r1)); c = ((255-s2)/ (255-r2)); k = 0:r1; y1 = a*k; plot (k,y1); hold on; k = r1: r2; y2 = b*(k - r1) + a*r1; plot (k,y2); k = r2+1:255; y3 = c*(k-r2) + b*(r2-r1)+a*r1; plot (k,y3); xlim([0 255]); ylim([0 255]); xlabel('input gray level, r'); ylabel('outphut gray level, s'); title('Form of transformation'); hold on; figure; f = imread('Fig3.10(b).jpg'); [m, n] = size (f); for i = 1:m for j = 1:n if((f(i,j)>=0) & (f(i,j)<=r1)) g(i,j) = a*f(i,j); else if((f(i,j)>r1) & (f(i,j)<=r2)) g(i,j) = ((b*(f(i,j)-r1)+(a*r1))); else if((f(i,j)>r2) & (f(i,j)<=255)) g(i,j) = ((c*(f(i,j)-r2)+(b*(r2-r1)+(a*r1)))); end end end end end imshow(f), figure, imshow(g); % function thresholding >> f = imread('Fig3.10(b).jpg'); [m, n] = size(f); for i = 1:m for j = 1:n if((f(i,j)>=0) & (f(i,j)<128))
- 9. 8 g(i,j) = 0; else g(i,j) = 255; end end end imshow(f), figure, imshow(g); (a) Form of contrast stretching transformation function. (b) A low-contrast image. (c) Result of contrast stretching. (d) Result of thresholding a b c d
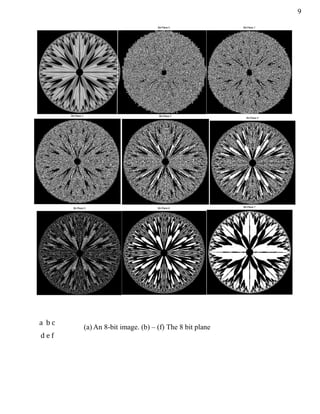
- 10. 9 (a) An 8-bit image. (b) – (f) The 8 bit plane a b c d e f
- 11. 10 3.3.1 Histogram equalization The transformation function of histogram equalization is ( ) ∑ ( ) ∑ k = 0, 1, …, L – 1. % Histogram; f1 = imread('Fig3.15(a)1top.jpg'); f2 = imread('Fig3.15(a)2.jpg'); f3 = imread('Fig3.15(a)3.jpg'); f4 = imread('Fig3.15(a)4.jpg'); f = input('image: '); imhist(f), figure; g = histeq(f, 256); imshow(g), figure, imhist(g); a b c Fig. 3.17 Transformation functions (1) through (4) were obtained from the images in Fig. 3.17 (a), using histogram equalization
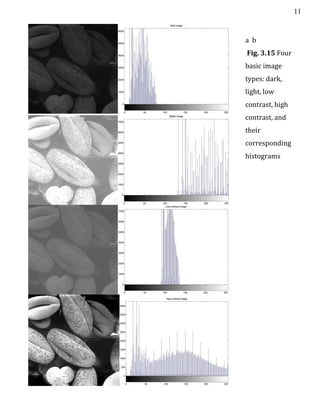
- 12. 11 a b Fig. 3.15 Four basic image types: dark, light, low contrast, high contrast, and their corresponding histograms
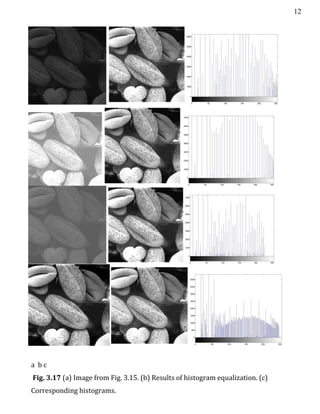
- 13. 12 a b c Fig. 3.17 (a) Image from Fig. 3.15. (b) Results of histogram equalization. (c) Corresponding histograms.
- 14. 13 3.4.2 Subtraction The difference between tow images f (x, y) and h (x, y), expressed as g (x, y) = f (x, y) – h (x, y), The commands, f1 = imread('Fig3.28.a.jpg'); f2 = imread('Fig3.28.b.jpg'); f3 = imsubtract(f1,f2); f4 = histeq(f3,256); imshow(f3), figure, imshow(f4); a b c d Fig. 3.17 (a) The first image. (b) The second image. (c) Difference between (a) and (b). (d) Histogram – equalized difference image.
- 15. 14 3.6.1 Smoothing Linear Filters The commands, f = imread('Fig3.35(a).jpg'); w3 = 1/ (3. ^2)*ones (3); g3 = imfilter (f, w3, 'conv', 'replicate', 'same'); w5 = 1/ (5. ^2)*ones (5); g5 = imfilter (f, w5, 'conv', 'replicate', 'same'); w9 = 1/ (9. ^2)*ones (9); g9 = imfilter (f, w9, 'conv', 'replicate', 'same'); w15 = 1/ (15. ^2)*ones (15); g15 = imfilter (f, w15, 'conv', 'replicate', 'same'); w35 = 1/ (35. ^2)*ones (35); g35 = imfilter(f, w35, 'conv', 'replicate', 'same'); imshow (g3), figure, imshow (g5), figure, imshow (g9), figure, imshow (g15), figure, imshow (g35), figure; h = imread ('Fig3.36(a).jpg'); h15 = imfilter (h, w15, 'conv', 'replicate', 'same'); [m, n] = size (h15); for i = 1:m for j = 1:n if ((h15 (i,j)>=0) & (h15 (i,j)<128)) g (i,j) = 0; else g(i,j) = 255; end end end imshow(h15), figure, imshow(g);
- 16. 15 Fig. 3.35 (a) Original image, of size 500 x 500 pixels. (b) – (f) Result of smoothing with square averaging filter masks of size n = 3, 5, 9, 15, and 35 respectively. a b c d e f
- 17. 16 3.6.2 Order-Statistics Filters The commands, >> f = imread('Fig3.37(a).jpg'); w3 = 1/(3.^2)*ones(3); g3 = imfilter(f, w3, 'conv', 'replicate', 'same'); g = medfilt2(g3); imshow(g3), figure, imshow(g); a b c Fig. 3.36 (a) Original image. (b) Image processed by a 15 x 15 averaging mask. (c) Result of thresholding (b) Fig. 3.37 (a) X – ray image of circuit board corrupted by salt – and – pepper noise. (b) Noise reduction with a 3 x 3 averaging mask. (c) Noise reduction with a 3 x 3 median filter a b c
- 18. 17 3.7.2 The Laplacian The Laplacian for image enhancement is as follows: ( ) { ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) The commands, % Laplacian function f1 = imread('Fig3.40(a).jpg'); w4 = fspecial('laplacian', 0); g1 = imfilter(f1, w4, 'replicate'); imshow(g1, [ ]), figure; f2 = im2double(f1); g2 = imfilter(f2, w4, 'replicate'); imshow(g2, [ ]), figure; g3 = imsubtract(f2,g2); imshow(g3) Fig. 3.40 (a) Image of the North Pole of the moon. (b) Laplacian image scaled for display purposes. (d) Image enhanced by Eq. (3.7 – 5) a b c d
- 19. 18 % Laplacian simplication f1 = imread ('Fig3.41(c).jpg'); w5 = [0 -1 0; -1 5 -1; 0 -1 0]; g1 = imfilter (f1, w5, 'replicate'); imshow (g1), figure; w9 = [-1 -1 -1; -1 9 -1; -1 -1 -1]; g2 = imfilter (f1, w9, 'replicate'); imshow (g2); 0 -1 0 -1 5 -1 0 -1 0 -1 -1 -1 -1 9 -1 -1 -1 -1 a b c d e Fig. 3.37 (a) Composite Laplacian mask. (b) A second composite mask. (c) Scanning electron microscope image. (d) and (e) Result of filtering with the masks in (a) and (b) respectively.
- 20. 19 3.7.3 The Gradient The commands, >> f1 = imread('Fig3.45(a).jpg'); w = fspecial('sobel'); g1 = imfilter(f1, w, 'replicate'); imshow(g1); a b Fig. 3.45 (a) Optical image of contact lens (note defects on the boundary at 4 and 5 o’clock). (b) Sobel gradient

![NATIONAL CHENG KUNG UNIVERSITY
Inst. of Manufacturing Information & Systems
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING AND SOFTWARE
IMPLEMENTATION
HOMEWORK 1
Professor name: Chen, Shang-Liang
Student name: Nguyen Van Thanh
Student ID: P96007019
Class: P9-009 Image Processing and Software Implementation
Time: [4] 2 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-operators-140529193837-phpapp01/85/Digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-and-operators-1-320.jpg)

![2
PROBLEM
影像處理與軟體實現[HW1]
課程碼:P953300 授課教授:陳響亮 教授 助教:陳怡瑄 日期:2011/03/10
題目:請以C# 撰寫一程式,可讀入一影像檔,並可執行以下之影像
空間強化功能。
a. 每一程式需設計一適當之人機操作介面。
b. 每一功能請以不同方法分開撰寫,各項參數需讓使用者自行輸入。
c. 以C# 撰寫時,可直接呼叫Matlab 現有函式,但呼叫多寡,將列為評分考量。
(呼叫越少,分數越高)
一、 基本灰階轉換
1. 影像負片轉換
2. Log轉換
3. 乘冪律轉換
4. 逐段線性函數轉換
二、 直方圖處理
1. 直方圖等化處理
2. 直方圖匹配處理
三、 使用算術/邏輯運算做增強
1. 影像相減增強
2. 影像平均增強
四、 平滑空間濾波器
1. 平滑線性濾波器
2. 排序統計濾波器
五、 銳化空間濾波器
1. 拉普拉斯銳化空間濾波器
2. 梯度銳化空間濾波器](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-operators-140529193837-phpapp01/85/Digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-and-operators-3-320.jpg)
![3
SOLUTION
Using Matlab for solving the problem
3.2.1 Negative transformation
Given an image (input image) with gray level in the interval [0, L-1], the negative of that
image is obtained by using the expression: s = (L – 1) – r,
Where r is the gray level of the input image, and s is the gray level of the output.
In Matlab, we use the commands,
>> f=imread('Fig3.04(a).jpg');
g = imcomplement(f);
imshow(f), figure, imshow(g)
In/output image Out/in image
3.2.2 Log transformation
The Logarithm transformations are implemented using the expression:
s = c*log (1+r).
In this case, c = 1. The commands,
>> f=imread('Fig3.05(a).jpg');
g=im2uint8 (mat2gray (log (1+double (f))));
imshow(f), figure, imshow(g)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-operators-140529193837-phpapp01/85/Digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-and-operators-4-320.jpg)
![4
In/output image Out/in image
3.2.3 Power-law transformation
Power-law transformations have the basic form,
s = c*r. ^, where c and are positive constants.
The commands,
>> f = imread ('Fig3.08(a).jpg');
f = im2double (f);
[m n]=size (f);
c = 1;
gama = input('gama value = ');
for i=1:m
for j=1:n
g(i,j)=c*(f(i,j)^gama);
end
end;
imshow(f),figure, imshow(g);
With = 0.6, 0.4 and 0.3 respectively, we can get three images respectively, as shown in the
following figure,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-operators-140529193837-phpapp01/85/Digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-and-operators-5-320.jpg)

![7
3.2.4 Piecewise-linear transformation
Contrast stretching
The commands,
% function contrast stretching;
>> r1 = 100; s1 = 40;
r2 = 141; s2 = 216;
a = (s1/r1);
b = ((s2-s1)/ (r2-r1));
c = ((255-s2)/ (255-r2));
k = 0:r1;
y1 = a*k;
plot (k,y1); hold on;
k = r1: r2;
y2 = b*(k - r1) + a*r1;
plot (k,y2);
k = r2+1:255;
y3 = c*(k-r2) + b*(r2-r1)+a*r1;
plot (k,y3);
xlim([0 255]);
ylim([0 255]);
xlabel('input gray level, r');
ylabel('outphut gray level, s');
title('Form of transformation');
hold on; figure;
f = imread('Fig3.10(b).jpg');
[m, n] = size (f);
for i = 1:m
for j = 1:n
if((f(i,j)>=0) & (f(i,j)<=r1))
g(i,j) = a*f(i,j);
else
if((f(i,j)>r1) & (f(i,j)<=r2))
g(i,j) = ((b*(f(i,j)-r1)+(a*r1)));
else
if((f(i,j)>r2) & (f(i,j)<=255))
g(i,j) = ((c*(f(i,j)-r2)+(b*(r2-r1)+(a*r1))));
end
end
end
end
end
imshow(f), figure, imshow(g);
% function thresholding
>> f = imread('Fig3.10(b).jpg');
[m, n] = size(f);
for i = 1:m
for j = 1:n
if((f(i,j)>=0) & (f(i,j)<128))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-operators-140529193837-phpapp01/85/Digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-and-operators-8-320.jpg)



![14
3.6.1 Smoothing Linear Filters
The commands,
f = imread('Fig3.35(a).jpg');
w3 = 1/ (3. ^2)*ones (3);
g3 = imfilter (f, w3, 'conv', 'replicate', 'same');
w5 = 1/ (5. ^2)*ones (5);
g5 = imfilter (f, w5, 'conv', 'replicate', 'same');
w9 = 1/ (9. ^2)*ones (9);
g9 = imfilter (f, w9, 'conv', 'replicate', 'same');
w15 = 1/ (15. ^2)*ones (15);
g15 = imfilter (f, w15, 'conv', 'replicate', 'same');
w35 = 1/ (35. ^2)*ones (35);
g35 = imfilter(f, w35, 'conv', 'replicate', 'same');
imshow (g3), figure, imshow (g5), figure, imshow (g9), figure, imshow
(g15), figure, imshow (g35), figure;
h = imread ('Fig3.36(a).jpg');
h15 = imfilter (h, w15, 'conv', 'replicate', 'same');
[m, n] = size (h15);
for i = 1:m
for j = 1:n
if ((h15 (i,j)>=0) & (h15 (i,j)<128))
g (i,j) = 0;
else
g(i,j) = 255;
end
end
end
imshow(h15), figure, imshow(g);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-operators-140529193837-phpapp01/85/Digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-and-operators-15-320.jpg)


![17
3.7.2 The Laplacian
The Laplacian for image enhancement is as follows:
( )
{
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( )
The commands,
% Laplacian function
f1 = imread('Fig3.40(a).jpg');
w4 = fspecial('laplacian', 0);
g1 = imfilter(f1, w4, 'replicate');
imshow(g1, [ ]), figure;
f2 = im2double(f1);
g2 = imfilter(f2, w4, 'replicate');
imshow(g2, [ ]), figure;
g3 = imsubtract(f2,g2);
imshow(g3)
Fig. 3.40 (a) Image of
the North Pole
of the moon.
(b) Laplacian
image scaled
for display
purposes. (d)
Image
enhanced by
Eq. (3.7 – 5)
a b
c d](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-operators-140529193837-phpapp01/85/Digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-and-operators-18-320.jpg)
![18
% Laplacian simplication
f1 = imread ('Fig3.41(c).jpg');
w5 = [0 -1 0; -1 5 -1; 0 -1 0];
g1 = imfilter (f1, w5, 'replicate');
imshow (g1), figure;
w9 = [-1 -1 -1; -1 9 -1; -1 -1 -1];
g2 = imfilter (f1, w9, 'replicate');
imshow (g2);
0 -1 0
-1 5 -1
0 -1 0
-1 -1 -1
-1 9 -1
-1 -1 -1
a b c
d e
Fig. 3.37 (a) Composite Laplacian mask. (b) A second composite
mask. (c) Scanning electron microscope image. (d) and (e)
Result of filtering with the masks in (a) and (b) respectively.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-operators-140529193837-phpapp01/85/Digital-image-processing-using-matlab-basic-transformations-filters-and-operators-19-320.jpg)
