JavaScript for ABAP Programmers - 2/7 Data Types
- 1. JavaScript for ABAP Programmers Data Types Chris Whealy / The RIG
- 2. ABAP Strongly typed Syntax similar to COBOL Block Scope No equivalent concept OO using class based inheritance Imperative programming JavaScript Weakly typed Syntax derived from Java Lexical Scope Functions are 1st class citizens OO using referential inheritance Imperative or Functional programming
- 3. Strongly Typed vs. Weakly Typed Languages There are two schools of thought for determining how data should be stored in variables: • ABAP uses Strong (or Static) Typing Apart from field symbols, all ABAP variables must have their data type defined at declaration time © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 3
- 4. Strongly Typed vs. Weakly Typed Languages There are two schools of thought for determining how data should be stored in variables: • ABAP uses Strong (or Static) Typing • JavaScript uses Weak (or Dynamic) Typing Apart from field symbols, all ABAP variables A variable takes on the data type of whatever must have their data type defined at declaration value it currently holds time © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 4
- 5. Strongly Typed vs. Weakly Typed Languages There are two schools of thought for determining how data should be stored in variables: • ABAP uses Strong (or Static) Typing • JavaScript uses Weak (or Dynamic) Typing Apart from field symbols, all ABAP variables A variable takes on the data type of whatever must have their data type defined at declaration value it currently holds time • Pros and Cons of Strong Typing + Data type errors can be trapped at compile time - Rigid type systems reduce language flexibility © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 5
- 6. Strongly Typed vs. Weakly Typed Languages There are two schools of thought for determining how data should be stored in variables: • ABAP uses Strong (or Static) Typing • JavaScript uses Weak (or Dynamic) Typing Apart from field symbols, all ABAP variables A variable takes on the data type of whatever must have their data type defined at declaration value it currently holds time • Pros and Cons of Strong Typing • Pros and Cons of Weak Typing + Data type errors can be trapped at compile time - Rigid type systems reduce language flexibility - Data type errors can only be trapped at runtime + Highly flexible type system allows for a dynamic style of coding © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 6
- 7. Strongly Typed vs. Weakly Typed Languages There are two schools of thought for determining how data should be stored in variables: • ABAP uses Strong (or Static) Typing • JavaScript uses Weak (or Dynamic) Typing Apart from field symbols, all ABAP variables A variable takes on the data type of whatever must have their data type defined at declaration value it currently holds time • Pros and Cons of Strong Typing • Pros and Cons of Weak Typing + Data type errors can be trapped at compile time - Rigid type systems reduce language flexibility - Data type errors can only be trapped at runtime + Highly flexible type system allows for a dynamic style of coding Compiled languages (E.G. ABAP, Java, C) tend to use strong typing, whereas interpreted scripting languages (E.G. JavaScript, Ruby, Python) tend to use weak typing. © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 7
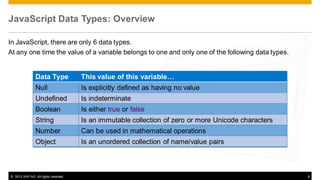
- 8. JavaScript Data Types: Overview In JavaScript, there are only 6 data types. At any one time the value of a variable belongs to one and only one of the following data types. Data Type This value of this variable… Null Is explicitly defined as having no value Undefined Is indeterminate Boolean Is either true or false String Is an immutable collection of zero or more Unicode characters Number Can be used in mathematical operations Object Is an unordered collection of name/value pairs © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 8
- 9. JavaScript Data Types 1/3 In the coding, the data types are specified as follows: // -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Special null; // Indicates an explicit non-value undefined; // Indicates an indeterminate value (E.G. a variable is declared but not initialised) © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 9
- 10. JavaScript Data Types 1/3 In the coding, the data types are specified as follows: // -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Special null; // Indicates an explicit non-value undefined; // Indicates an indeterminate value (E.G. a variable is declared but not initialised) // -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Boolean true; false; © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 10
- 11. JavaScript Data Types 1/3 In the coding, the data types are specified as follows: // -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Special null; // Indicates an explicit non-value undefined; // Indicates an indeterminate value (E.G. a variable is declared but not initialised) // -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Boolean true; false; // -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// String – contains zero or more Unicode characters 'Bazinga!'; // Can be delimited by either single quotes ""; // Or double quotes © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 11
- 12. JavaScript Data Types 2/3 In the coding, the data types are specified as follows: // -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Number 3.1415926; // Stored as 64-bit floating point number 1; // Be careful, this is stored as floating point value, not an integer! © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 12
- 13. JavaScript Data Types 2/3 In the coding, the data types are specified as follows: // -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Number 3.1415926; // Stored as 64-bit floating point number 1; // Be careful, this is stored as floating point value, not an integer! // Warning! All the usual problems associated with trying to represent decimal values in binary // floating point format still apply in JavaScript! var result = 0.1 + 0.2; result; // 0.30000000000000004, not 0.3 (Decimal 0.1 has no exact binary equivalent) © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 13
- 14. JavaScript Data Types 2/3 In the coding, the data types are specified as follows: // -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Number 3.1415926; // Stored as 64-bit floating point number 1; // Be careful, this is stored as floating point value, not an integer! // Warning! All the usual problems associated with trying to represent decimal values in binary // floating point format still apply in JavaScript! var result = 0.1 + 0.2; result; // 0.30000000000000004, not 0.3 (Decimal 0.1 has no exact binary equivalent) // Special numerical values that could be returned in the event of illegal mathematical operations // (These values are actually stored as properties of the Global Object) NaN; // 'Not a Number' E.G. 1/'cat' NaN Infinity; // The result of division by zero © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 14
- 15. JavaScript Data Types 3/3 In addition to the basic data type of Object, JavaScript provides several built-in objects that behave as if they were composite data types. E.G. Array, Date, Function, Math and RegEx etc. // -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Object. Zero or more unordered name:value pairs of any data type delimited by curly braces { pet1: 'cat', pet2: 'dog' }; © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 15
- 16. JavaScript Data Types 3/3 In addition to the basic data type of Object, JavaScript provides several built-in objects that behave as if they were composite data types. E.G. Array, Date, Function, Math and RegEx etc. // -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Object. Zero or more unordered name:value pairs of any data type delimited by curly braces { pet1: 'cat', pet2: 'dog' }; // Array object. Zero or more values of any data type accessed by a numerical, 0 based index [1,2,3,4,5]; © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 16
- 17. JavaScript Data Types 3/3 In addition to the basic data type of Object, JavaScript provides several built-in objects that behave as if they were composite data types. E.G. Array, Date, Function, Math and RegEx etc. // -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Object. Zero or more unordered name:value pairs of any data type delimited by curly braces { pet1: 'cat', pet2: 'dog' }; // Array object. Zero or more values of any data type accessed by a numerical, 0 based index [1,2,3,4,5]; // Function object. A special object that has both properties and executable content function() { /* statements */ } © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 17
- 18. JavaScript Data Types 3/3 In addition to the basic data type of Object, JavaScript provides several built-in objects that behave as if they were composite data types. E.G. Array, Date, Function, Math and RegEx etc. // -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Object. Zero or more unordered name:value pairs of any data type delimited by curly braces { pet1: 'cat', pet2: 'dog' }; // Array object. Zero or more values of any data type accessed by a numerical, 0 based index [1,2,3,4,5]; // Function object. A special object that has both properties and executable content function() { /* statements */ } // Math object. Contains many useful mathematical functions and constants Math.PI; // 3.141592653589793 © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 18
- 19. JavaScript Data Types 3/3 In addition to the basic data type of Object, JavaScript provides several built-in objects that behave as if they were composite data types. E.G. Array, Date, Function, Math and RegEx etc. // -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Object. Zero or more unordered name:value pairs of any data type delimited by curly braces { pet1: 'cat', pet2: 'dog' }; // Array object. Zero or more values of any data type accessed by a numerical, 0 based index [1,2,3,4,5]; // Function object. A special object that has both properties and executable content function() { /* statements */ } // Math object. Contains many useful mathematical functions and constants Math.PI; // 3.141592653589793 // Regular Expression Object. A tool for specifying and extracting patterns of text within a string /^(?:([A-Za-z]+):)?(/{0,3})([0-9.-A-Za-z]+)(?::(d+))?(?:/([^?#]*))?(?:?([^#]*))?(?:#(.*))?$/; © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 19
- 20. JavaScript Data Types 3/3 In addition to the basic data type of Object, JavaScript provides several built-in objects that behave as if they were composite data types. E.G. Array, Date, Function, Math and RegEx etc. // -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Object. Zero or more unordered name:value pairs of any data type delimited by curly braces { pet1: 'cat', pet2: 'dog' }; // Array object. Zero or more values of any data type accessed by a numerical, 0 based index [1,2,3,4,5]; // Function object. A special object that has both properties and executable content function() { /* statements */ } // Math object. Contains many useful mathematical functions and constants Math.PI; // 3.141592653589793 // Regular Expression Object. A tool for specifying and extracting patterns of text within a string // Regular expressions are sometimes confused with Egyptian hieroglyphics... :-) © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 20
- 21. Variables and Data Types In weakly typed languages such as JavaScript, there is no concept of declaring that a variable should hold data of a particular type. The data type of a variable is determined simply by the value it currently holds. // A weakly typed language means that data types are determined // dynamically at runtime, not statically at design time var whoAmI = 'Hello world'; © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. // Variable 'whoAmI' is both declared & assigned a string value 21
- 22. Variables and Data Types In weakly typed languages such as JavaScript, there is no concept of declaring that a variable should hold data of a particular type. The data type of a variable is determined simply by the value it currently holds. // A weakly typed language means that data types are determined // dynamically at runtime, not statically at design time var whoAmI = 'Hello world'; // Variable 'whoAmI' is both declared & assigned a string value whoAmI = 1.61792; whoAmI = [1,2,3,4,5]; // Now it's a number // Now it's an array © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 22
- 23. Variables and Data Types In weakly typed languages such as JavaScript, there is no concept of declaring that a variable should hold data of a particular type. The data type of a variable is determined simply by the value it currently holds. // A weakly typed language means that data types are determined // dynamically at runtime, not statically at design time var whoAmI = 'Hello world'; // Variable 'whoAmI' is both declared & assigned a string value whoAmI = 1.61792; whoAmI = [1,2,3,4,5]; // Now it's a number // Now it's an array whoAmI = true; // Now it's a Boolean © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 23
- 24. Variables and Data Types In weakly typed languages such as JavaScript, there is no concept of declaring that a variable should hold data of a particular type. The data type of a variable is determined simply by the value it currently holds. // A weakly typed language means that data types are determined // dynamically at runtime, not statically at design time var whoAmI = 'Hello world'; // Variable 'whoAmI' is both declared & assigned a string value whoAmI = 1.61792; whoAmI = [1,2,3,4,5]; // Now it's a number // Now it's an array whoAmI = true; // Now it's a Boolean whoAmI = { // Now it's an object someProperty: 'Hello world' } © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. 24
- 25. Variables and Data Types In weakly typed languages such as JavaScript, there is no concept of declaring that a variable should hold data of a particular type. The data type of a variable is determined simply by the value it currently holds. // A weakly typed language means that data types are determined // dynamically at runtime, not statically at design time var whoAmI = 'Hello world'; // Variable 'whoAmI' is both declared & assigned a string value whoAmI = 1.61792; whoAmI = [1,2,3,4,5]; // Now it's a number // Now it's an array whoAmI = true; // Now it's a Boolean whoAmI = { // Now it's an object someProperty: 'Hello world' } whoAmI = function() { }; © 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved. // Now it's a...you get the idea 25















![JavaScript Data Types 3/3
In addition to the basic data type of Object, JavaScript provides several built-in objects that behave as
if they were composite data types. E.G. Array, Date, Function, Math and RegEx etc.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Object. Zero or more unordered name:value pairs of any data type delimited by curly braces
{ pet1: 'cat',
pet2: 'dog' };
// Array object. Zero or more values of any data type accessed by a numerical, 0 based index
[1,2,3,4,5];
© 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved.
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js4ap02datatypes-140218120947-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-for-ABAP-Programmers-2-7-Data-Types-16-320.jpg)
![JavaScript Data Types 3/3
In addition to the basic data type of Object, JavaScript provides several built-in objects that behave as
if they were composite data types. E.G. Array, Date, Function, Math and RegEx etc.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Object. Zero or more unordered name:value pairs of any data type delimited by curly braces
{ pet1: 'cat',
pet2: 'dog' };
// Array object. Zero or more values of any data type accessed by a numerical, 0 based index
[1,2,3,4,5];
// Function object. A special object that has both properties and executable content
function() { /* statements */ }
© 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved.
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js4ap02datatypes-140218120947-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-for-ABAP-Programmers-2-7-Data-Types-17-320.jpg)
![JavaScript Data Types 3/3
In addition to the basic data type of Object, JavaScript provides several built-in objects that behave as
if they were composite data types. E.G. Array, Date, Function, Math and RegEx etc.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Object. Zero or more unordered name:value pairs of any data type delimited by curly braces
{ pet1: 'cat',
pet2: 'dog' };
// Array object. Zero or more values of any data type accessed by a numerical, 0 based index
[1,2,3,4,5];
// Function object. A special object that has both properties and executable content
function() { /* statements */ }
// Math object. Contains many useful mathematical functions and constants
Math.PI; // 3.141592653589793
© 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved.
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js4ap02datatypes-140218120947-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-for-ABAP-Programmers-2-7-Data-Types-18-320.jpg)
![JavaScript Data Types 3/3
In addition to the basic data type of Object, JavaScript provides several built-in objects that behave as
if they were composite data types. E.G. Array, Date, Function, Math and RegEx etc.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Object. Zero or more unordered name:value pairs of any data type delimited by curly braces
{ pet1: 'cat',
pet2: 'dog' };
// Array object. Zero or more values of any data type accessed by a numerical, 0 based index
[1,2,3,4,5];
// Function object. A special object that has both properties and executable content
function() { /* statements */ }
// Math object. Contains many useful mathematical functions and constants
Math.PI; // 3.141592653589793
// Regular Expression Object. A tool for specifying and extracting patterns of text within a string
/^(?:([A-Za-z]+):)?(/{0,3})([0-9.-A-Za-z]+)(?::(d+))?(?:/([^?#]*))?(?:?([^#]*))?(?:#(.*))?$/;
© 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved.
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js4ap02datatypes-140218120947-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-for-ABAP-Programmers-2-7-Data-Types-19-320.jpg)
![JavaScript Data Types 3/3
In addition to the basic data type of Object, JavaScript provides several built-in objects that behave as
if they were composite data types. E.G. Array, Date, Function, Math and RegEx etc.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Object. Zero or more unordered name:value pairs of any data type delimited by curly braces
{ pet1: 'cat',
pet2: 'dog' };
// Array object. Zero or more values of any data type accessed by a numerical, 0 based index
[1,2,3,4,5];
// Function object. A special object that has both properties and executable content
function() { /* statements */ }
// Math object. Contains many useful mathematical functions and constants
Math.PI; // 3.141592653589793
// Regular Expression Object. A tool for specifying and extracting patterns of text within a string
// Regular expressions are sometimes confused with Egyptian hieroglyphics... :-)
© 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved.
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js4ap02datatypes-140218120947-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-for-ABAP-Programmers-2-7-Data-Types-20-320.jpg)

![Variables and Data Types
In weakly typed languages such as JavaScript, there is no concept of declaring that a variable should hold data of
a particular type. The data type of a variable is determined simply by the value it currently holds.
// A weakly typed language means that data types are determined
// dynamically at runtime, not statically at design time
var whoAmI = 'Hello world';
// Variable 'whoAmI' is both declared & assigned a string value
whoAmI = 1.61792;
whoAmI = [1,2,3,4,5];
// Now it's a number
// Now it's an array
© 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved.
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js4ap02datatypes-140218120947-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-for-ABAP-Programmers-2-7-Data-Types-22-320.jpg)
![Variables and Data Types
In weakly typed languages such as JavaScript, there is no concept of declaring that a variable should hold data of
a particular type. The data type of a variable is determined simply by the value it currently holds.
// A weakly typed language means that data types are determined
// dynamically at runtime, not statically at design time
var whoAmI = 'Hello world';
// Variable 'whoAmI' is both declared & assigned a string value
whoAmI = 1.61792;
whoAmI = [1,2,3,4,5];
// Now it's a number
// Now it's an array
whoAmI = true;
// Now it's a Boolean
© 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved.
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js4ap02datatypes-140218120947-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-for-ABAP-Programmers-2-7-Data-Types-23-320.jpg)
![Variables and Data Types
In weakly typed languages such as JavaScript, there is no concept of declaring that a variable should hold data of
a particular type. The data type of a variable is determined simply by the value it currently holds.
// A weakly typed language means that data types are determined
// dynamically at runtime, not statically at design time
var whoAmI = 'Hello world';
// Variable 'whoAmI' is both declared & assigned a string value
whoAmI = 1.61792;
whoAmI = [1,2,3,4,5];
// Now it's a number
// Now it's an array
whoAmI = true;
// Now it's a Boolean
whoAmI = {
// Now it's an object
someProperty: 'Hello world'
}
© 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved.
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js4ap02datatypes-140218120947-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-for-ABAP-Programmers-2-7-Data-Types-24-320.jpg)
![Variables and Data Types
In weakly typed languages such as JavaScript, there is no concept of declaring that a variable should hold data of
a particular type. The data type of a variable is determined simply by the value it currently holds.
// A weakly typed language means that data types are determined
// dynamically at runtime, not statically at design time
var whoAmI = 'Hello world';
// Variable 'whoAmI' is both declared & assigned a string value
whoAmI = 1.61792;
whoAmI = [1,2,3,4,5];
// Now it's a number
// Now it's an array
whoAmI = true;
// Now it's a Boolean
whoAmI = {
// Now it's an object
someProperty: 'Hello world'
}
whoAmI = function() { };
© 2013 SAP AG. All rights reserved.
// Now it's a...you get the idea
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/js4ap02datatypes-140218120947-phpapp01/85/JavaScript-for-ABAP-Programmers-2-7-Data-Types-25-320.jpg)