LM7_ Embedded Sql and Dynamic SQL in dbms
- 1. Department of Computer Science and Engineering Name of the Faculty : Ms. Aruna T N Subject Name & Code : CS3492/ Database Management Systems Branch & Department : Computer Science and Engineering Year & Semester : II / IV CS3492/DBMS/IICSE/IVSEM/KG-KiTE KGiSL Institute of Technology (Approved by AICTE, New Delhi; Affiliated to Anna University, Chennai) Recognized by UGC, Accredited by NBA (IT) 365, KGiSL Campus, Thudiyalur Road, Saravanampatti, Coimbatore – 641035.
- 2. Course Outcome CO 1 Demonstrate fundamentals of Data models and Relational databases - K3 LEVEL CS3492/DBMS/IICSE/IVSEM/KG-KiTE
- 3. Syllabus UNIT I - RELATIONAL DATABASES Purpose of Database System – Views of data – Data Models – Database System Architecture – Introduction to relational databases – Relational Model – Keys – Relational Algebra – SQL fundamentals – Advanced SQL features – Embedded SQL– Dynamic SQL CS3492/DBMS/IICSE/IVSEM/KG-KiTE
- 5. Embedded SQL • The Programming module in which the SQL statements are embedded is called Embedded SQL module. • It is possible to embed SQL statements inside a variety of programming languages such as C, C++, Java, Fortran, and PL/1, • A language to which SQL queries are embedded is referred to as a host language. • EXEC SQL statement is used in the host language to identify embedded SQL request to the preprocessor EXEC SQL <embedded SQL statement >; CS3492/DBMS/IICSE/IVSEM/KG-KiTE
- 6. Embedded SQL(Cont.) • Before executing any SQL statements, the program must first connect to the database. This is done using: EXEC-SQL connect to server user user-name using password; Here, server identifies the server to which a connection is to be established. • Variables of the host language can be used within embedded SQL statements. They are preceded by a colon (:) to distinguish from SQL variables (e.g., :credit_amount ) • In some languages, like COBOL, the semicolon is replaced with END- EXEC • In Java embedding uses # SQL { …. }; CS3492/DBMS/IICSE/IVSEM/KG-KiTE
- 7. Embedded SQL(Cont.) • Variables used must be declared within DECLARE section, as illustrated below. The syntax for declaring the variables, however, follows the usual host language syntax. EXEC-SQL BEGIN DECLARE SECTION; int credit-amount ; EXEC-SQL END DECLARE SECTION; CS3492/DBMS/IICSE/IVSEM/KG-KiTE
- 8. Embedded SQL(Cont.) • To write an embedded SQL query, we use the declare c cursor for <SQL query> statement. The variable c is used to identify the query • Example: From within a host language, find the ID and name of students who have completed more than the number of credits stored in variable credit_amount in the host langue. CS3492/DBMS/IICSE/IVSEM/KG-KiTE
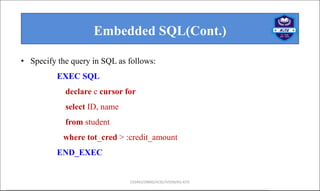
- 9. Embedded SQL(Cont.) CS3492/DBMS/IICSE/IVSEM/KG-KiTE • Specify the query in SQL as follows: EXEC SQL declare c cursor for select ID, name from student where tot_cred > :credit_amount END_EXEC
- 10. Embedded SQL(Cont.) • The open statement for our example is as follows: EXEC SQL open c ; • This statement causes the database system to execute the query and to save the results within a temporary relation. The query uses the value of the host- language variable credit-amount at the time the open statement is executed. • The fetch statement causes the values of one tuple in the query result to be placed on host language variables. EXEC SQL fetch c into :si, :sn END_EXEC CS3492/DBMS/IICSE/IVSEM/KG-KiTE
- 11. Embedded SQL(Cont.) CS3492/DBMS/IICSE/IVSEM/KG-KiTE • A variable called SQLSTATE in the SQL communication area (SQLCA) gets set to '02000' to indicate no more data is available • The close statement causes the database system to delete the temporary relation that holds the result of the query. EXEC SQL close c ; Note: above details vary with language. For example, the Java embedding defines Java iterators to step through result tuples.
- 12. Updates through Embedded SQL • Embedded SQL expressions for database modification (update, insert, and delete) • Can update tuples fetched by cursor by declaring that the cursor is for update EXEC SQL declare c cursor for select * from instructor where dept_name = 'Music' for update CS3492/DBMS/IICSE/IVSEM/KG-KiTE
- 13. Updates through Embedded SQL • We then iterate through the tuples by performing fetch operations on the cursor (as illustrated earlier), and after fetching each tuple we execute the following code: update instructor set salary = salary + 1000 where current of c
- 14. Dynamic SQL • The dynamic SQL component of SQL allows programs to construct and submit SQL queries at run time. • In contrast, embedded SQL statements must be completely present at compile time, they are compiled by the embedded SQL preprocessor. • Using dynamic SQL programs can create SQL queries as strings at runtime and can either have them executed immediately or have them prepared for sub sequent use.