Basic Concepts of OOPs (Object Oriented Programming in Java)
- 1. BASIC CONCEPTS OF OOPs Presented by: Michelle Anne Meralpis
- 2. JAVA • Java – a high-level programming language • Same with C, FORTRAN, Smalltalk, Perl • Lets you write special programs called Applets • Java is called as an Object-Oriented Programming Language
- 3. What is OOP? • Software Development Technique • Effective use of programmer productivity • Way of creating large scale systems • Approaching 100% solution
- 4. Basic Concepts of OOPs • Object • Class • Inheritance • Polymorphism • Encapsulation • Data Abstraction
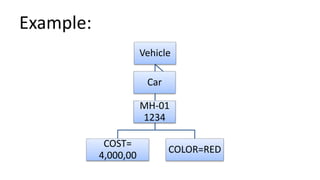
- 5. Object • A person, place or concepts • Composed of characteristics (data) and behavior (operation)
- 6. Example:
- 7. Class • A blueprint or prototype from which objects are created • A collection of objects of similar type
- 9. Example:
- 10. Inheritance • The process by which objects of one class can get properties of objects of another class.
- 11. Polymorphism • The ability to take more than one form • Allows us to write generic, reusable code more easily
- 12. Example:
- 13. Encapsulation • Wrapping of data and functions into a single unit (i.e. class) • Information hiding
- 14. Data Abstraction • Refers to the act of representing important description without including the background details or explanations
- 15. Creating Objects Point originOne = new Point(23,94); Rectangle rectOne = new Rectangle(originOne, 100, 200); Rectangle rectTwo = new Rectangle(50, 100); Each of these statements has three parts: 1. Declaration – the code set in bold are all variable declarations that associate a variable name with an object type. 2. Instantiation – the new keyword is a Java operator that creates the object. 3. Initialization: The new operator is followed by a call to a constructor, which initializes the new object.
- 16. Declaring Object Reference • Previously, you learned that to declare a variable, you write: type name; • You can also declare a reference variable on its own line. For example: Point originOne;
- 17. Instantiating a Class • The new operator returns a reference to the object it created. This reference is usually assigned to a variable of the appropriate type, like: Point originOne = new Point(23, 94); • It can also be used directly in an expression. For example: int height = new Rectangle().height;
- 18. Initializing an Object • Here's the code for the Point class: public class Point { public int x = 0; public int y = 0; //constructor public Point(int a, int b) { x = a; y = b; } }
- 19. Initializing an Object (2) Point originOne = new Point(23, 94); • The result of executing this statement can be illustrated in the next figure:
- 20. Calling an Object's Methods • Append the method’s simple name to the object reference using intervening dot operator (.) • Provide arguments to the method within enclosing parenthesis () objectReference.methodName(argumentList); Or objectReference.methodName();
- 21. Calling an Object's Methods (2) new Rectangle(100, 50).getArea() • As shown, you can use the dot notation to invoke the new Rectangle’s getArea() method to compute the area of the new rectangle.