Python Programming Introduction demo.ppt
- 1. Introduction to Programming Language (Python)
- 2. • Programming languages are essential tools used to communicate instructions to computers. • They bridge the gap between human-readable code and machine-executable instructions.
- 3. Computer Languages • Machine Language • Uses binary code • Machine-dependent • Not portable • Assembly Language – Uses mnemonics – Machine-dependent – Not usually portable • High-Level Language (HLL) – Uses English-like language – Machine independent – Portable (but must be compiled for different platforms) – Examples: Python, C, C++, Java, Fortran, . . .
- 4. Compilation • Compiler translates source into target (a machine language program) • Compiler goes away at execution time • Compiler is itself a machine language program Compiler Target Program Source Program Target Program Input Output
- 5. Program Execution • Steps taken by the CPU to run a program (instructions are in machine language): 1. Fetch an instruction 2. Decode (interpret) the instruction 3. Retrieve data, if needed 4. Execute (perform) actual processing 5. Store the results, if needed
- 7. Program Errors • Syntax Errors: – Errors in grammar of the language • Runtime error: – When there are no syntax errors, but the program can’t complete execution • Divide by zero • Invalid input data • Logical errors: – The program completes execution, but delivers incorrect results – Incorrect usage of parentheses
- 8. How to use Python in your PC • You can install the python software from http://python.org/downloads/ • You can use the Python IDE (integrated development environment) like PyCharm, Anaconda, Jupiter notebook, etc. • You can use online Python compiler like www.onlinegdb.com
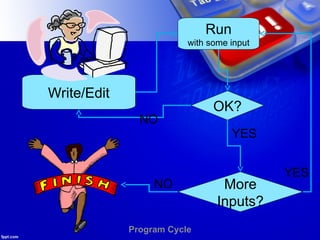
- 9. Ways to run the Python program 1. Running Python in interactive mode:
- 10. 2. Running Python in script mode: User Program Filename as Hello with extension as py
- 11. • Working with the interactive mode is better when Python programmers deal with small pieces of code as you can type and execute them immediately, but when the code is more than 2-4 lines, using the script for coding can help to modify and use the code in future
- 12. x,y = 6,10 if x < y: print (x) else: print (y) print (‘is the min’) x y 6 10 Run the program Output 6 Indentation • Indentation is important in Python – grouping of statement (block of statements) – no explicit brackets, e.g. { }, to group statements skipped
- 13. INPUT ( ) FUNCTION INPUT ( ) FUNCTION
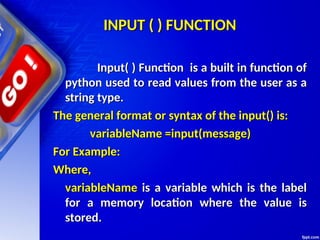
- 14. INPUT ( ) FUNCTION INPUT ( ) FUNCTION Input( ) Function is a built in function of Input( ) Function is a built in function of python used to read values from the user as a python used to read values from the user as a string type. string type. The general format or syntax of the input() is: The general format or syntax of the input() is: variableName =input(message) variableName =input(message) For Example: For Example: Where, Where, variableName variableName is a variable which is the label is a variable which is the label for a memory location where the value is for a memory location where the value is stored. stored.
- 15. INPUT ( ) FUNCTION INPUT ( ) FUNCTION For Example: For Example: p = input(“Enter the value”) p = input(“Enter the value”) Note: it will read the value as string (non-numeric). Note: it will read the value as string (non-numeric). x = int(input(“Enter x value”)) x = int(input(“Enter x value”)) reads the value and converts it in to integer type reads the value and converts it in to integer type data or value. data or value. y=float(input(“Enter y value”)) y=float(input(“Enter y value”)) reads the value and converts it in to float type reads the value and converts it in to float type data or value. data or value.
- 16. INPUT ( ) FUNCTION INPUT ( ) FUNCTION int ( ) and float ( ) Functions: int ( ) and float ( ) Functions: Python offers two functions to be used Python offers two functions to be used with input( ) to convert the received values: with input( ) to convert the received values: Example 1: Example 1: >>age = int(input(“Enter age”)) >>age = int(input(“Enter age”)) Example 2: Example 2: >>sal=float(input(“Enter salary)) >>sal=float(input(“Enter salary))
- 17. PRINT ( ) FUNCTION PRINT ( ) FUNCTION
- 18. PRINT ( ) FUNCTION PRINT ( ) FUNCTION print( ) print( ) Function is a built in function of Function is a built in function of python used to display the values on the python used to display the values on the screen screen The general format or syntax of the input() is: The general format or syntax of the input() is: Print(“message”, variable) Print(“message”, variable) The print function can print an arbitrary The print function can print an arbitrary number of values ("value1, value2, ..."), which are number of values ("value1, value2, ..."), which are separated by commas. These values are separated separated by commas. These values are separated by blanks. In the following example we can see by blanks. In the following example we can see two print calls. We are printing two values in both two print calls. We are printing two values in both cases, i.e. a string and a float number: cases, i.e. a string and a float number:
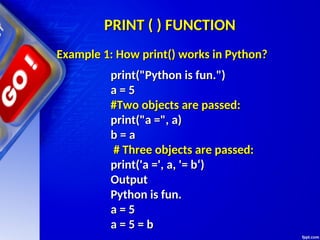
- 19. PRINT ( ) FUNCTION PRINT ( ) FUNCTION print("Python is fun.") print("Python is fun.") a = 5 a = 5 #Two objects are passed: #Two objects are passed: print("a =", a) print("a =", a) b = a b = a # Three objects are passed: # Three objects are passed: print('a =', a, '= b‘) print('a =', a, '= b‘) Output Output Python is fun. Python is fun. a = 5 a = 5 a = 5 = b a = 5 = b Example 1: How print() works in Python? Example 1: How print() works in Python?
- 20. PRINT ( ) FUNCTION PRINT ( ) FUNCTION >>> print("a = ", a) >>> print("a = ", a) a = 3.564 a = 3.564 >>> print("a = n", a) >>> print("a = n", a) a = a = 3.564 3.564 >>> >>> Example 2: How print() works in Python? Example 2: How print() works in Python?
- 21. Simple problems in Python: • Print “Hello Word!” • Add two integer numbers • Multiplication of two numbers. • Compute average of 3 numbers. • Find area of rectangle. • Find area of square • Find area of circle • Find perimeter of rectangle.
- 22. Any Questions Please Any Questions Please